ラザルス ミハエル

Gliosomnia and immunity: decoding brain-immune interactions in sleep
研究内容
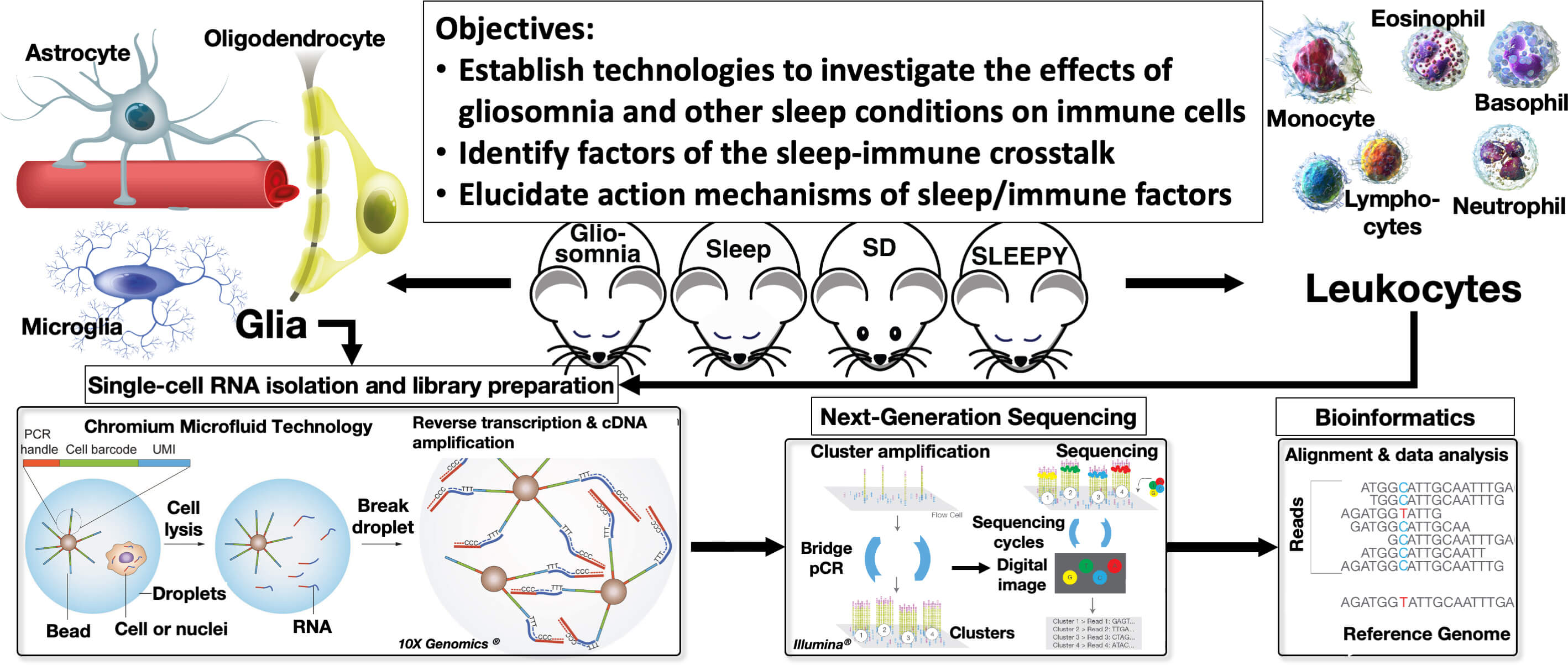
Glial cells exhibit great diversity and function beyond merely maintaining brain homeostasis. They can actively influence neural outcomes by mediating neuronal functions. One intriguing possibility of this glia-neuron interaction is the regulation of sleep, as emerging evidence suggests that glial cells may have a much more significant impact on sleep homeostasis than previously thought. Furthermore, studies have shown that immune cell differentiation and proliferation are synchronized with sleep. However, the molecular and cellular mechanisms that underlie the regulation of the immune system by sleep, including the potential contribution of glia to the regulation of sleep (gliosomnia), remain unclear. This project aims to comprehensively analyze gene expression in glia from the nucleus accumbens, a novel brain area responsible for the integration and regulation of sleep and motivation, as well as in leukocytes from peripheral blood of wild-type mice, sleep-deprived mice, and mutant mice with gliosomnia or high sleep need. Using single-cell gene expression analysis, the study will identify and characterize candidate molecules that interfere with the regulation of the immune system. The project aims to obtain important insights into the regulation of the immune system by sleep homeostasis, with glia responsible for stimulating both sleep and the immune system. Ultimately, this project aims to demonstrate that immune resilience is a critical function of the sleeping brain.
研究概略図
代表業績
• Lin Y, Roy K, Shuji I, Otani R, Amezawa M, Ishikawa Y, Chérasse Y, Kaushik MK, Klewe-Nebenius D, Zhou L, Yanagisawa Y, Oishi Y, *Saitoh T, *Lazarus M. (2023) Positive allosteric adenosine A2A receptor modulation suppresses insomnia associated with mania- and schizophrenia-like behaviors in mice, Frontiers in Pharmacology, 14: doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138666.
• Zhou X, Oishi Y, Cherasse Y, Korkutata M, Fujii S, Lee CY, *Lazarus M. (2019) Extracellular adenosine and slow-wave sleep are increased after ablation of nucleus accumbens core astrocytes and neurons in mice. Neurochemistry International, 124, 256-263.
• Korkutata M, Saitoh T, Cherasse Y, Ioka S, Duo F, Qin R, Murakoshi N, Fujii S, Zhou X, Sugiyama F, Chen JF, Kumagai H, Nagase H, *Lazarus M. (2019) Enhancing endogenous adenosine A2A receptor signaling induces slow-wave sleep without affecting body temperature and cardiovascular function. Neuropharmacology, 144, 122-132.
• Takata Y, Oishi Y, Zhou XZ, Hasegawa E, Takahashi K, Cherasse Y, Sakurai T, *Lazarus M> (2018) Sleep and wakefulness are controlled by ventral medial midbrain/pons GABAergic neurons in mice. Journal of Neuroscience, 38, 10080-10092.
• Oishi Y, Xu Q, Wang L, Zhang BJ, Takahashi K, Takata Y, Luo YJ, Cherasse Y, Schiffmann SN, de Kerchove d’Exaerde A, Urade Y, Qu WM, Huang ZL, *Lazarus M> (2017) Slow-wave sleep is controlled by a subset of nucleus accumbens core neurons in mice. Nature Communications, 8, article 734, doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00781-4